Everyone knows vegetables are good for them, but why is this true? The short answer is that they are good for you because they are what you should be eating. But that answer doesn’t tell us much, and more importantly, there are lessons that can be learned from understanding just why vegetables are so good for our bodies.
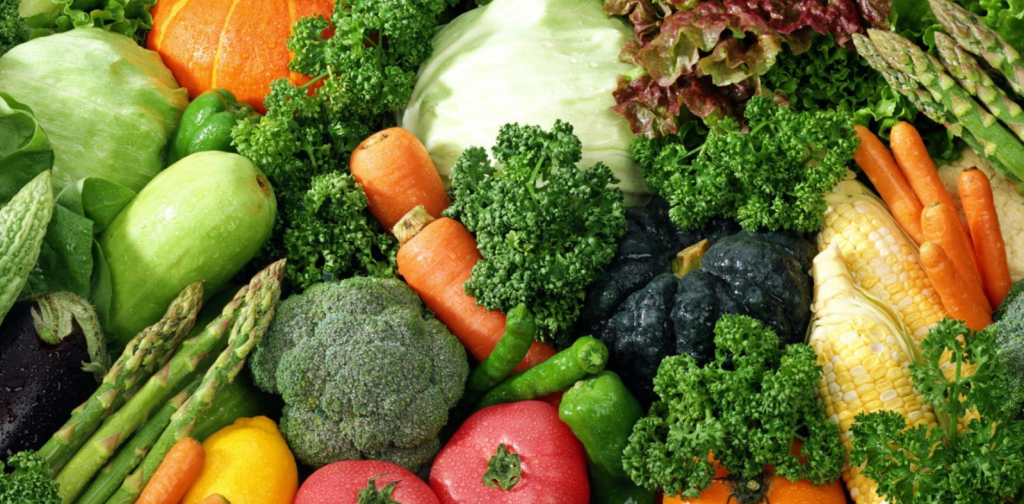

Let’s take a look at exactly what makes vegetables so good for you.
High Nutrition, Low Calories
Anyone who reads this blog regularly knows I’m not a big fan of the calorie concept (see: When it Comes to Weight Loss, Forget Calories), but calories are useful when talking about certain food concepts and understanding the goodness of vegetables is one of those times.
There are many ways to measure the value of the food you are eating. Measuring food by weight and nutrients is called a Nutrient Adequacy Score and is a common way to measure the quality of food, but it is very inaccurate. You can also measure the quality of food by calorie (called a Nutrient Density Score): how many nutrients food supplies per calorie. The Nutrient Density Score is much more accurate.
When you compare the nutritional value of foods by calories you see that nothing stacks up to vegetables.
When you calculate the Nutrient Density of Foods then foods such as kale, spinach, Brussels sprouts score really high (you get a lot of nutrients per calorie) and foods like grains, beans, and even meats are much lower (not many nutrient per calorie).
There are many different nutrient density scoring charts, but the most user-friendly is Dr. Joel Furhman’s (see ANDI Scoring System). Using this system show you that there is nothing as good for you to eat as fruits and vegetables.
You might be shunning vegetables for their taste or cost, but take a closer look. Vegetables may seem expensive, but they provide the best nutrient per calorie of almost any food[i]
Anti-Everything
Vegetables are the anti-everything food (anti-cancer, anti-heart disease…) There are no better fighters of disease to put in your mouth than fruits and vegetables. Let’s take a look.
Anticancer
- Eating more veggies protects against cancer of the stomach and pancreas as well as colorectal, prostate,[iii] and bladder cancers. Even lung cancer risk is lower for smokers who eat their veggies.[iv]
- For women, cancers of the cervix, ovary, and breast,[v] and endometrium are all lower when they consume more vegetables.
- Women who consume a large amount of fiber are at lower risk for breast cancer in women (fiber “sweeps” cholesterol and bad estrogens out of the body).[vi]
- Clinical trials are ongoing with many individual fruits and vegetables:
- Compounds found in vegetables are also being tested: lycopene (from tomatoes), sulforaphane (from asparagus), brassinin, (from cruciferous vegetables), indole-3-carbinol (from broccoli), and resveratrol (from grapes and peanuts). [xi]
-
John Hopkins School Of Medicine has been studying the benefits of Brassica vegetables for over 20 years.
- High vegetable consumption reduces your risk of high blood pressure.[xii]
- A high-fiber diet lowers cholesterol,[xiii]
- You also reduce your overall risk of heart disease when you eat your veggies.[xiv]
- Consumption of fruits and vegetables—particularly leafy green vegetables and vitamin C-rich fruits—appears to have a protective effect against coronary heart disease.[xv]
- Eating more vegetables helps you to lose weight; scientific research has shown that eating more fiber does help to lower your weight.[xvi]
Heart Disease
- High vegetable consumption reduces your risk of high blood pressure.[i]
- A high-fiber diet lowers cholesterol,[ii]
- You also reduce your overall risk of heart disease when you eat fruits and veggies.[iii]
- Consumption vegetables—particularly leafy green vegetables—appears to have a protective effect against coronary heart disease.[iv]
Weight Loss
- Eating more vegetables helps you to lose weight; scientific research has shown that eating more fiber does help to lower your weight.[v]
Other Diseases
- The risk for Alzheimer’s, [xvii] diabetes, [xviii] and many other diseases is lower with higher vegetable consumption.
Vegetables are Good For You
There is no doubt that vegetables and fruits are good for you, the research above is only a tiny bit of what is out there. You should try to make vegetables as much of your diet as possible. You can feed your body what it needs by making sure every meal has some sort of vegetable.
[i] Darmon N, Darmon M, Maillot M, Drewnowski A. A nutrient density standard for vegetables and fruits: nutrients per calorie and nutrients per unit cost. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005 Dec;105(12):1881-7.
[ii] Riboli E, Norat T. Epidemiologic evidence of the protective effect of fruit and vegetables on cancer risk. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003 Sep;78(3 Suppl):559S-569S.
[iii] Freedland SJ, Aronson WJ. Dietary intervention strategies to modulate prostate cancer risk and prognosis. Curr Opin Urol. 2009 May;19(3):263-7.
[iv] Block G, Patterson B, Subar A. Fruit, vegetables, and cancer prevention: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 1992;18(1):1-29.
[v] Patterson RE, Cadmus LA, Emond JA, Pierce JP. Physical activity, diet, adiposity and female breast cancer prognosis: A review of the epidemiologic literature. Maturitas. 2010 Jan 22
[vi] Suzuki R, Rylander-Rudqvist T, Ye W, Saji S, Adlercreutz H, Wolk A. Dietary fiber intake and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer defined by estrogen and progesterone receptor status–a prospective cohort study among Swedish women. Int J Cancer. 2008 Jan 15;122(2):403-12.
[vii] Herr I, Büchler MW. Dietary constituents of broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables: implications for prevention and therapy of cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010 Aug;36(5):377-83. Epub 2010 Feb 20.
[viii] Bianchini F, Vainio H. Allium vegetables and organosulfur compounds: do they help prevent cancer? Environ Health Perspect. 2001 Sep;109(9):893-902
[ix] Ansari MS, Ansari S. Lycopene and prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 2005 Jun;1(3):425-30.
[x] Gullett NP, Ruhul Amin AR, Bayraktar S, Pezzuto JM, et al. Cancer prevention with natural compounds. Semin Oncol. 2010 Jun;37(3):258-81.
[xi] Gullett NP, Ruhul Amin AR, Bayraktar S, Pezzuto JM, et al. Cancer prevention with natural compounds. Semin Oncol. 2010 Jun;37(3):258-81.
[xii] Alonso A, de la Fuente C, Martín-Arnau AM, et al. Fruit and vegetable consumption is inversely associated with blood pressure in a Mediterranean population with a high vegetable-fat intake: the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra (SUN) Study. Br J Nutr. 2004 Aug;92(2):311-9.
[xiii] Brown L, Rosner B, Willett WW, Sacks FM. Cholesterol-lowering effects of dietary fiber: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999 Jan;69(1):30-42.
[xiv] Slavícek J, Kittnar O, Fraser GE, et al. Lifestyle decreases risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2008 Dec;16(4):161-4.
[xv] Joshipura KJ, Hu FB, Manson JE, et al. The effect of fruit and vegetable intake on risk for coronary heart disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001 Jun 19;134(12):1106-14.
[xvi] Liu S, Willett WC, Manson JE, et al. Relation between changes in intakes of dietary fiber and grain products and changes in weight and development of obesity among middle-aged women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003 Nov;78(5):920-7.
[xvii] Giem P, Beeson WL, Fraser GE. The incidence of dementia and intake of animal products: preliminary findings from the Adventist Health Study. Neuroepidemiology. 1993;12(1):28-36.
[xviii] Barnard ND, Cohen J, Jenkins DJ, et al. A low-fat vegan diet and a conventional diabetes diet in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled, 74-wk clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 May;89(5):1588S-1596S. Epub 2009 Apr 1.











Yes
i think that fruits and vegetables are good for us because they give us nutrients and energy. i think that schools should lower the price for fruit and raise the price of chips and other unhealthy stuff. 60 cents for fruit and 50 cents for chips…that is rediculous!!
Couldn’t agree with you more MacKenzee!